Understanding the OWASP Mobile Top 10 Security Risks in Mobile Apps
Mobile applications have become an integral part of daily life, handling everything from banking transactions to personal communication. With this widespread adoption comes an increasing responsibility to protect sensitive information. Cyberattacks on mobile apps are rising, and businesses must prioritize security from the very beginning of development.
The OWASP Mobile Top 10 is a globally recognized standard that highlights the most critical vulnerabilities affecting mobile applications. By understanding these risks, developers and organizations can build safer, more reliable apps for users.
What Is the OWASP Mobile Top 10?

The OWASP Mobile Top 10 serves as a benchmark for identifying and mitigating the most significant threats to mobile applications. It is widely adopted across industries as a guideline for developing secure apps. These risks range from improper platform usage to vulnerabilities in cryptography, authentication, and network communication. Following the Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP helps businesses maintain trust with users and prevent costly security breaches.
The list is not just a theoretical framework; it provides actionable steps and best practices for developers. Understanding the Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP enables teams to prioritize the most pressing threats and implement proactive security measures throughout the app lifecycle.
Improper Platform Usage
Improper platform usage is one of the key risks identified in the Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP. Mobile operating systems, such as iOS and Android, provide built-in security features, including secure storage, encryption libraries, and permission controls. However, developers sometimes misconfigure or ignore these mechanisms, leaving sensitive data exposed. Ensuring proper usage of platform-specific security tools is essential. For example, secure storage through iOS Keychain or Android Keystore must be implemented correctly to prevent unauthorized access.
Insecure Data Storage
Insecure data storage is another major concern. Mobile apps often store sensitive information, such as credentials, personal data, and payment details. If this data is stored in plain text or weakly encrypted, attackers can easily access it. The Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP recommends robust encryption practices, minimizing local storage, and avoiding unnecessary retention of sensitive information. Secure storage practices protect users and help organizations comply with privacy regulations.
Weak Authentication and Authorization

Weak authentication and authorization can allow attackers to bypass security measures and access confidential information. Passwords that are easy to guess, a lack of multi-factor authentication, and improper session handling can all lead to unauthorized access. The Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP emphasizes implementing strong authentication mechanisms, enforcing secure session management, and ensuring that users can only access resources they are authorized for. These practices are essential for safeguarding user accounts and sensitive app functionalities.
Insecure Network Communication
Mobile apps interact frequently with servers, APIs, and third-party services. Insecure transmission of data over networks can expose sensitive information to interception. The Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP highlights the importance of secure communication, including HTTPS, certificate pinning, and regular network audits. Protecting data in transit ensures that user information remains confidential and prevents attacks such as man-in-the-middle exploits.
Code Vulnerabilities and Reverse Engineering
Mobile apps can be reverse-engineered to reveal sensitive information, manipulate app behavior, or bypass security controls. The Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP recommends using code obfuscation, tamper detection, and runtime protections to secure application logic. Protecting the code from reverse engineering preserves intellectual property and prevents malicious modifications that could compromise app security.
Client-Side Injection Risks
Client-side injection attacks occur when apps improperly handle untrusted input, allowing attackers to inject malicious commands or scripts. Examples include SQL injection, JavaScript injection, or unintended file operations. Secure coding practices, input validation, and thorough testing are necessary to defend against such attacks. The Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP stresses the importance of mitigating injection risks to protect both users and the application.
Insufficient Cryptography
Many mobile applications fail to implement cryptography correctly or rely on outdated algorithms, leaving sensitive data vulnerable. The Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP recommends adopting modern encryption standards and regularly reviewing cryptographic implementations. Proper cryptography ensures data confidentiality and strengthens overall app security, reducing the risk of breaches and unauthorized access.
Security Misconfigurations
Security misconfigurations are common yet preventable risks. Apps shipped with default settings, excessive permissions, or enabled debugging features can be exploited by attackers. The Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP advises conducting regular audits, applying strict configuration management, and following secure deployment practices. Minimizing misconfigurations improves app resilience and protects user data.
Insufficient Protection Against Reverse Engineering and Tampering
Apps lacking measures against tampering or reverse engineering are vulnerable to unauthorized modifications and security bypasses. Techniques such as binary encryption, runtime protection, and integrity verification help mitigate these risks. The Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP emphasizes protecting apps from tampering to maintain trust, safeguard sensitive functionality, and ensure data integrity.
Implementing a Holistic Mobile App Security Strategy
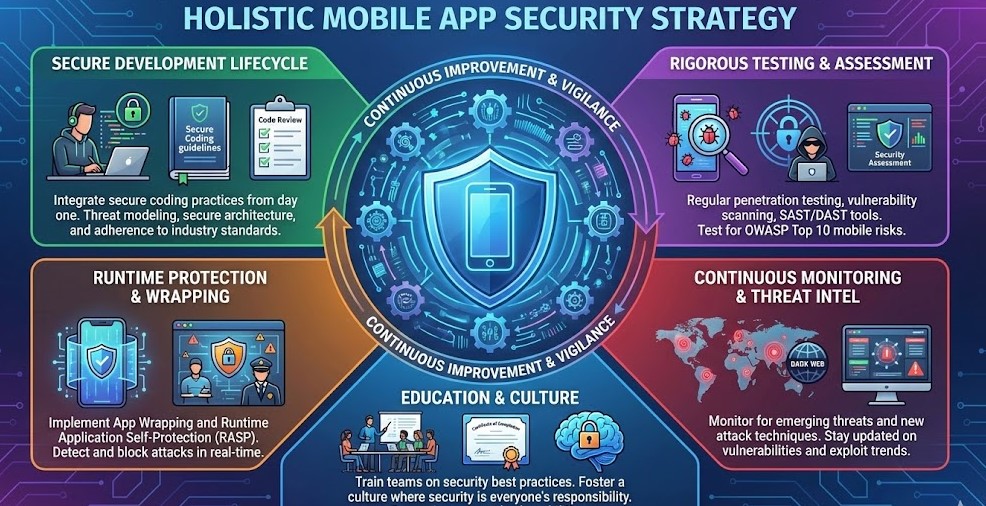
Addressing vulnerabilities requires more than individual fixes. Developers should integrate secure coding practices, rigorous testing, app wrapping, and runtime application self-protection into their workflow. Regular security assessments, penetration testing, and monitoring for emerging threats are essential. Understanding the Top 10 Mobile Security Risks by OWASP is the foundation, but continuous vigilance and proactive measures ensure long-term app security.
Education is equally important. Teams should be trained to recognize potential vulnerabilities, adhere to best practices, and stay updated on new attack techniques. By embedding security into the development culture, organizations can reduce risk and deliver apps that users trust
Conclusion
The OWASP Mobile Top 10 provides a critical framework for understanding and mitigating the most significant mobile app security risks. From improper platform usage to insufficient cryptography and reverse engineering, each risk requires careful attention and proactive solutions. By adopting secure development practices, regular testing, and holistic strategies, developers and businesses can build mobile apps that are not only functional but resilient against evolving threats. Prioritizing mobile security protects users, maintains trust, and enhances the overall success of applications.
Doverunner offers enterprise-grade mobile app security solutions that include advanced app wrapping, runtime protection, and code hardening. Their services help businesses safeguard applications from hacking, reverse engineering, and data breaches. With seamless integration, expert deployment support, and continuous monitoring, DoveRunner ensures robust protection without compromising app performance, empowering companies to deliver secure and reliable mobile experiences at scale.